Disinvestment refers to the sale or liquidation of assets by the government, usually Central and state public sector enterprises, projects, or other fixed assets. The government undertakes disinvestment to reduce the fiscal burden on the exchequer, or to raise money for meeting specific needs, such as to bridge the revenue shortfall from other regular sources. In some cases, disinvestment may be done to privatize assets. However, not all disinvestment is privatization.
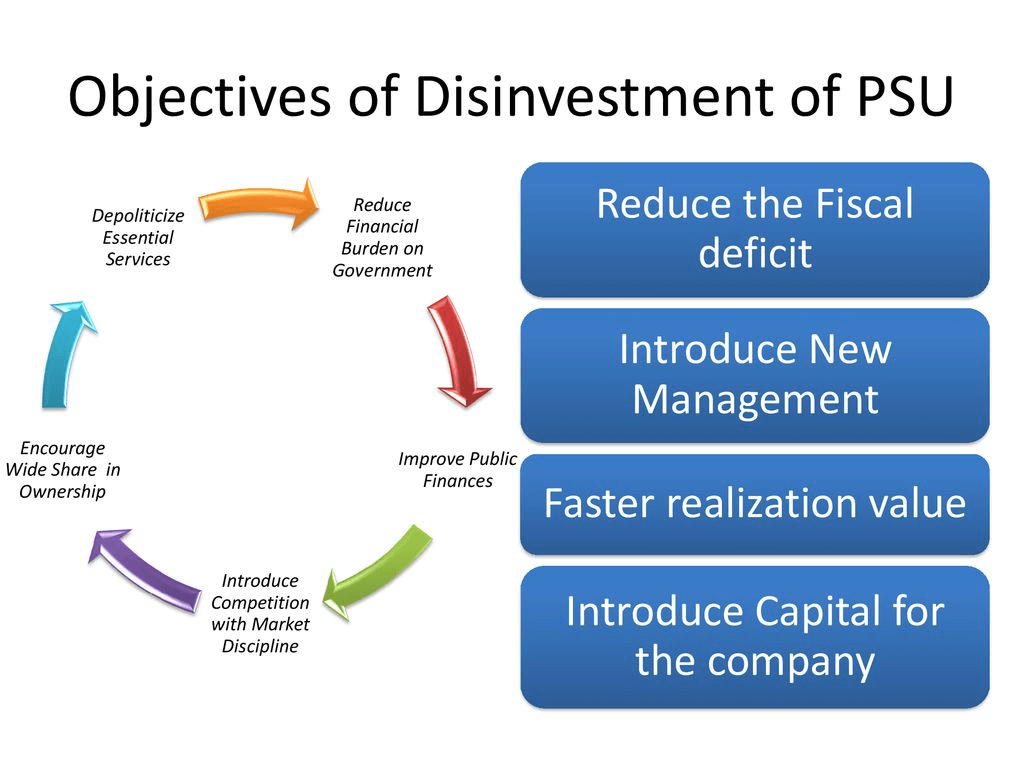
Objectives of disinvestment
- Reduce the fiscal burden on the exchequer
- Improve public finances
- Encourage private ownership
- Fund growth and development programs
- Maintain and promote competition in the market
Benefits of disinvestment
- Helpful in the long-term growth of the country
- Allows the government and even the company to reduce debt
- Encourages private ownership of assets and trading in the open market
- Allows for the development of a strong capital market in India
- If successful, it means that the government does not have to fund the losses of a loss-making unit anymore
Methods of Disinvestment
- Different methods of disinvestment include:
- Initial Public Offering (IPO)
- Further Public Offering (FPO)
- Offer for sale (OFS)
- Strategic sale
- Institutional Placement Program (IPP)
- CPSE Exchange Traded Fund (ETF)
- IPO is an offer of shares by an unlisted central public sector enterprise (CPSE) or the government out of its shareholding or a combination of both to the public for subscription for the first time.
- FPO is an offer of shares by a listed CPSE or the government out of its shareholding or a combination of both to the public for subscription.
- OFS is the sale of shares by promoters through the Stock Exchange mechanism.
- A strategic sale is the sale of a substantial portion of the government shareholding of a CPSE, of up to 50% or such higher percentage as the competent authority may determine, along with transfer of management control.
- An IPP is where only institutions can participate in the offering.
- Disinvestment through ETF route allows simultaneous sale of GoI’s stake in various CPSEs across diverse sectors through a single offering.
Challenges in Disinvestment and the Current Scenario
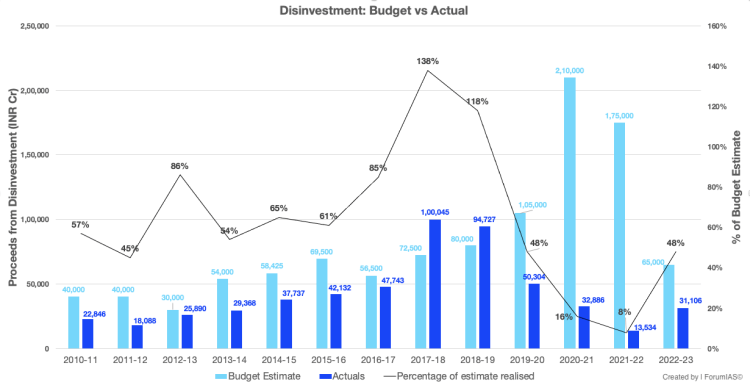
The Finance Ministry pared the disinvestment target for 2023-24 to a nine-year low of ₹51,000 crore and publicly acknowledged the multiple challenges it is facing in privatizing public sector enterprises (PSEs) and raising funds through minority stake sales, a drive that has stalled since Air India’s sale. In 2021-22, when Air India was added to the Tata group, the Centre missed its high disinvestment target of ₹1.75 lakh crore by a significant margin, raising just ₹13,534 crore in disinvestment proceeds.
The sale of the 52.8% stake in Bharat Petroleum (BPCL) had to be called off in mid-2022 because almost all the bidders had withdrawn. The strategic sale of Central Electronics was also shelved due to lapses in the bidding process, and the Pawan Hans stake-sale did not take off as well.
Why In News
he disinvestment target for 2023-24 has been lowered by the Finance Ministry to a nine-year low of ₹51,000 crore, and the Ministry has openly recognized the various obstacles it is encountering in the process of privatizing public sector enterprises (PSEs) and raising funds through minority stake sales. This initiative has been at a standstill since the sale of Air India.
MCQs on Disinvestment Methods in India
-
What is the main objective of disinvestment in India?
A. Reduce the fiscal burden on the exchequer
B. Fund only growth and development programs
C. Discourage private ownership
D. Increase debt burden
-
Which of the following is not a method of disinvestment in India?
A. Initial Public Offering (IPO)
B. Offer for sale (OFS)
C. Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
D. Strategic sale
-
What is an IPO in the context of disinvestment in India?
A. Offer of shares by an unlisted CPSE or the government to the public for subscription for the first time
B. Sale of shares by promoters through the Stock Exchange mechanism
C. Sale of a substantial portion of the government shareholding of a CPSE with transfer of management control
D. Sale of shares by a listed CPSE or the government to the public for subscription
-
What was the reason for the reduction of the disinvestment target for 2023-24?
A. Multiple challenges faced in privatising public sector enterprises
B. Increase in the fiscal burden on the exchequer
C. Successful privatisation of public sector enterprises
D. Increase in the number of CPSEs
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


